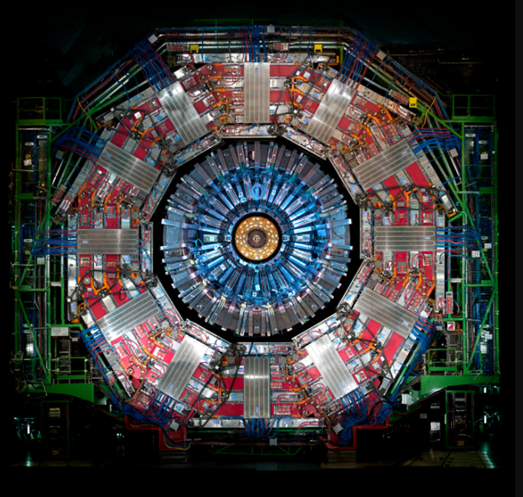
There are a lot of experiments going on in CERN including the LHC experiments which got us Higgs boson.
Scientists from all over the world carry out experimental collaborations and research programs ensuring CERN covering wide topics of physics. Finding the answer to the questions unanswered and finding new questions with new challenges. Topics like the Standard Model, supersymmetry to Antimatter, and cosmic rays are observed and studied.
Using LHC and other sophisticated instruments at CERN, a lot of experiments are being done, like Fixed target experiment, Atlas Experiment, Antimatter experiment.
In this article, we are going to know about some important experiments going on at CERN.
Fixed-Target Experiment
In this experiment, a charged particle is accelerated with the help of an electric field and collides with a target. Then the detector determines the physical quantities of the resulting particles.
An example would be that of the Rutherford Gold foil experiment, in which high-energy alpha particles are bombarded on thin gold foil (Fixed target). The result of this experiment was the existence of a nucleus in atoms. The detector used in the gold foil experiment was Zinc – sulfide screen.
Fixed target experiments have been the backbone of the lab’s physics activities at CERN. Some notable experiments among these were fed by Super Proton Synchrotron.
Some important projects under Fixed target experiments-
- Compass

In this experiment, physicists study the ways about how elementary particles like quarks and gluons work together to form matter as we know. From a proton to the exotic particle.
Studying the internal structure of protons and neutrons is a major aim of this experiment and to discover how spin arises in these particles, how they contribute to the motion of quarks.
This is done by firing muons (heavy electrons) and pions at a polarized target.
2. Cloud

CLOUD stands for cosmic leaving outdoor droplets. The scientist has always wondered if cosmic rays affect climate change and if they do how. With this experiment, they might be able to answer that.
Just like the name, this experiment involves cloud, but here comes a fun fact. This cloud is made artificially in a 3-inch stainless steel box under similar conditions as in the atmosphere. Gases go through pipes, UV light is there to act as sun, iodine particles are added which has been found out to be significant in forming aerosols in clouds.
All this is monitored through a sensitive spectrometer and their changes are recorded.
The purpose of this experiment is to understand aerosol in clouds is formed, and how climate is affected by cosmic rays.
Antimatter Experiment
British physicist Paul Dirac wrote an equation in 1928 for which he won a noble prize in 1933, relating quantum theory and special relativity to better describe the motion of an electron. But this equation can have two solutions.
- Electron with positive energy
- Electron with negative energy.
But we knew that the energy of a particle can only be a positive number.
Dirac concluded that for every particle as we know there exists an antiparticle. Like for every electron there exist a positive electron (which we know now as a positron).
Thus, Scientists speculated that during the big bang matter and antimatter both would have been produced but we see only matter around us. So where did the antimatter go?
Using the Antiproton Decelerator which slows antiprotons physicists at CERN investigates its properties and other aspects of anti-matter that opened with the Dirac’s equation.
Some important Antimatter experiments are –
- ALPHA

ALPHA stand for Antihydrogen Laser physics apparatus.
The major purpose of this experiment is to make antihydrogen, know the process of containing it for a longer period and compare its properties with hydrogen atoms.
This experiment is the successor of an earlier experiment called Athena. It used a different method to trap the antihydrogen atoms before they annihilate with ordinary atoms.
Making antihydrogen depends on bringing two particles together. One is the Antiprotons and the other is the position. Together they are trapped in a device for charged particles.
And on June 2011, it succeeded in holding antihydrogen for over 16 minutes.
Giving physicists more time to study the antimatter mystery.
2. Base

BASE stands for Baryon Antibaryon Experiment.
Under this experiment, physicists compare the magnetic moments of protons and antiprotons to find out about the difference between matter and antimatter. And to figure out the age-old question, why there is more matter than antimatter in the universe?
In June 2014, It reported the first proton magnetic moment with a precision of 3.3 parts per billion. This team took new measurements of antiproton during the beamtime in 2014 at CERN’s Antiproton decelerator.
3. LHC Experiments
More than half a dozen experiments happen at CERN in Large hadron collider where detectors are used to analyse the properties of the particles produced due to the proton-proton collisions happening in the collider.
Each of these experiments is different from the other. Some are big like Atlas and CMU some are small like Totem and LHCf. These experiments are run with the collaborations of scientists from all over the world.
Many researchers hope that these experiments will help them answer some fundamental questions of physics, like gravity, the relation between quantum mechanics and general relativity, the structure of space and time.
Some of the important experiments of LHC are :
- Atlas

It is the largest general-purpose experiment at CERN. The experiment is intended to make use of the extraordinary energy available at the LHC to investigate events involving extraordinarily large particles that were previously unobservable using lower-energy accelerators. ATLAS was one of two LHC experiments involved in the July 2012 discovery of the Higgs boson.
2. CMS

CMS stands for compact muon solenoid the purpose of this experiment CMS’s purpose is to examine a wide spectrum of physics, including the hunt for the Higgs boson, additional dimensions, and particles that might be dark matter.
Although its goal might appear the same as Atlas it uses a different process for that.
More than 5000 scientists are involved in this project.
References used:
Fixed target, striking physics – CERN Courier














