Understanding the basics behind new discovery:
Researchers have discovered that serotonin, a neurotransmitter commonly associated with mood regulation, also plays a crucial role in visual processing in the thalamus of the brain. The thalamus is a key relay station that filters sensory information before it reaches the cortex, which is responsible for higher-level processing.
Credit: Reggiani et al
The study, published in the journal Nature Neuroscience, found that serotonin acts as a “gatekeeper” that regulates the flow of visual information through the thalamus. Specifically, the researchers found that serotonin release inhibits the activity of thalamic neurons that respond to visual stimuli, effectively filtering out irrelevant or distracting information.
The findings shed new light on the complex interplay between different neurotransmitters and their role in shaping sensory processing. They could also have implications for the development of treatments for disorders such as depression and anxiety, which are associated with altered serotonin signaling.
A study investigating the possible effects of serotonin:
“Internal states are known to affect sensory perception and processing, but this was generally thought to occur in the cortex or thalamus,” Chinfei Chen, one of the researchers who carried out the study, told Medical Xpress. “One of our previous studies revealed that arousal can suppress certain visual information channels at an earlier stage of the visual pathway––at the connection between the mouse retina and the thalamus before the information even reaches the brain. This form of ‘filtering’ of information suggests a very efficient means of processing only relevant information.”
Past studies have also found that internal states, including arousal, are mediated by neuromodulatory systems in the brainstem and other areas below the cortex, including the serotonergic system. This is essentially the system responsible for regulating physiological states through the transmission of serotonin.
Chen, her collaborator Mark Andermann, and Jasmine Reggiani specifically explored the effects of serotonin on the early processing of visual information and its transfer from the eyes to the thalamus. To do this, they used a technique known as two-photon calcium imaging to track the activity of individual retinal axons in the brains of awake mice as they viewed visual images on a computer monitor. While examining the mice, the researchers also increased the release of serotonin in the thalamus, by optogenetically stimulating serotonergic neurons as they entered the thalamus.
Optogenetic stimulation is a research technique used to intensify the activity of a set of genetically defined neurons using light. “We chose to specifically focus on serotonin because our previous work on mouse brain slices showed that serotonin can suppress neurotransmitter release from the retinothalamic synapse through a specific serotonin receptor, the 5HT1b receptor,” Chen explained.
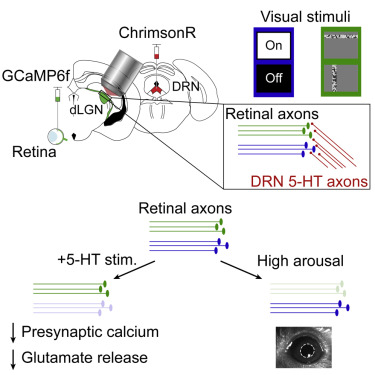
The experiments carried out by this team of researchers yielded very interesting results. Notably, they showed that serotonin can suppress calcium signals in retinal axons and the release of glutamate in the thalamus. This ultimately reduces the transmission of visual signals from the eye to the thalamus. When they analyzed their results more in detail, Andermann, Chen, and their colleagues found that some classes of retinal axons tended to be more suppressed by serotonin, with classes that responded to broad changes in light levels being more affected than those responding to fine visual details.
The researchers also compared the selective modulation observed in their experiments to that naturally occurring when animals or humans are highly aroused. They found that periods of high arousal that were not accompanied by an increase in the release of serotonin tended to suppress the retinal axons transmitting information about fine details, rather than changes in light levels. Overall, the results of this study confirm that different internal states can impact the processing of separate types of visual information.
In the future, this insight could inform new studies exploring the impact of neuromodulatory systems on downstream brain areas and on perception in animal models and humans, potentially leading to interesting new discoveries. “We now plan to continue investigating how serotonin alters thalamic output to the cortex by considering other components of the connections between the cortex and the thalamus that process the incoming retinal information,” Chen added. “Additionally, we will explore the effects of other known neuromodulators of the retinothalamic connection, including inhibitory transmission.”
Reference: Jasmine D.S. Reggiani et al, Brainstem serotonin neurons selectively gate retinal information flow to thalamus, Neuron (2022). DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2022.12.006














