A satellite mega-constellations is referred to as a group of artificial satellites performing as a system. A constellation can give lasting worldwide or close to worldwide coverage, with the end goal that whenever wherever on Earth, in any event, one satellite is visible. Satellites are regularly positioned in arrangements of reciprocal orbital planes and interface with all around the world distributed ground stations. They may likewise utilize inter-satellite correspondence.
The GPS constellation allows 24 satellites to be equally distributed among six orbital planes. It is noticeable how the quantity of satellites in view from an allotted point on the Earth’s surface, in this instance at 40°N, changes with time.
Different utilizations for satellite constellations comprise tracking, telecommunications and location awareness systems, military and government espionage, and monitoring. These instances are the Russian Federation’s Global Navigation Satellite System (GLONASS), Direct Broadcast Satellite (DBS) systems, Global Positioning Systems (GPS), and satellite-based Lidar.
Satellite groups of stars are additionally being utilized for broadband Internet and satellite telephone and phone networks. In spite of the fact that the performance isn’t yet equivalent to that of contemporary landlines, in circumstances where satellite-based networking might be the one option for those with no access to wireless services or terrestrial wired, the compromises included can be more than tolerable.
The majority of communications satellite constellations are geosynchronous, which implies they are parked in an orbit over the equator at an elevation synchronized with the pivot of the Earth beneath. Despite the fact that the satellites seem to dwell in similar areas in the sky consistently, there is actually a round-trip delay of a little more than a half-second, and this latency can result in frustration while communicating in real-time. Sending various satellites to overlap coverage can avoid latency.
Satellite constellations ought not to be mistaken for satellite clusters, which are groups of satellites moving near one another in practically indistinguishable orbits, satellite programs, which are known as generations of satellites inaugurated in progression, and satellite fleets, which are groups of satellites from the very producer or administrator that work autonomously from one another (not as a system).
NASA launched a constellation of micro-satellites from an airplane in December of 2016. The constellation which is known as the Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System measures surface breezes at the focal point of typhoons, tropical cyclones, and hurricanes.
Private Companies in Launching of Satellite Mega Constellation
SpaceX
SpaceX, Elon Musk’s private spaceflight company has been caught up with building the world’s biggest satellite internet constellation. Since May 2019, SpaceX has begun launching its new Starlink internet satellites in batches of 60, to make a “mega constellation” with a huge nImber of 30,000 little satellites.
If estimated accurately, this will particularly profit the 2.5 billion individuals who currently have no internet access. So far just around 800 satellites have been launched and it appears to be just the military has joined to utilize them, yet in 2021, SpaceX expects to have enough satellites and adequate ground-based infrastructure to give near-global coverage.
The effect of this will be that, regardless of where somebody is on the planet, rural or urban, they will have the option to get internet access. Also, it will be quick – up to a gigabit for each second, with latencies from 25 to 35 milliseconds, as per the company. This is because of the way that Starlink satellites will work at a moderately low circle of 550km.

Source:https://www.geekwire.com/2019/spacex-fcc-starlink-million-earth-stations/
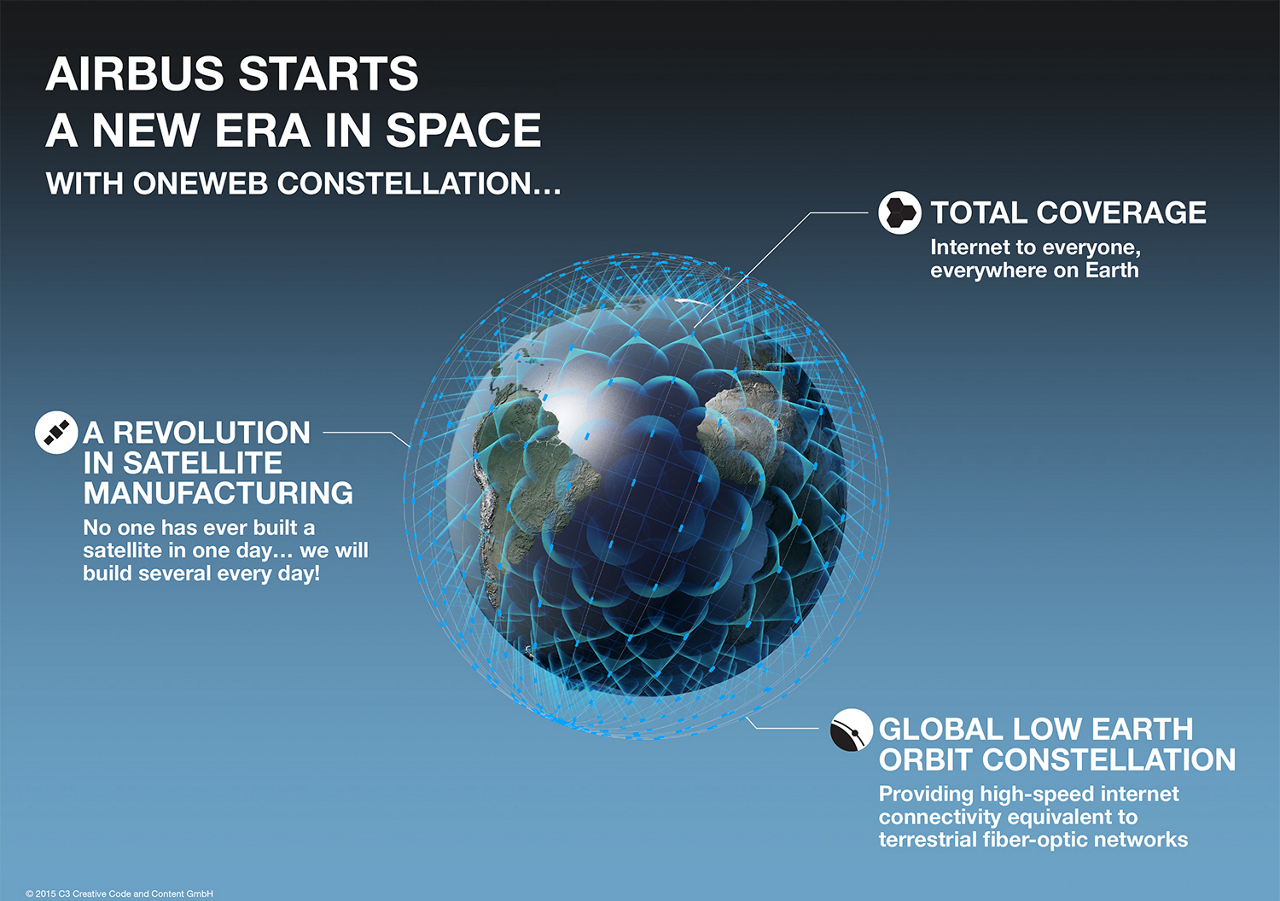
OneWeb
On 27 February 2019, OneWeb effectively launched the initial 6 of the 648 arranged satellites into low Earth orbit from the Center Spatial Guyanais utilizing a Russian Soyuz ST-B rocket.
Likewise, on the same day at the Mobile World Congress (MWC2019), OneWeb declared that it signed its initial two client contracts with Telia Company for their Quika low inactivity broadband service to the Middle East and the Africa and Informatica for service to Europe, denoting the start of its commercialization.
Amazon
Amazon is joining the chart of companies arranging a constellation of thousands of satellites for broadband internet connectivity. Amazon hasn’t revealed who might build the satellites or when they would be launched and hasn’t yet categorized with the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) for U.S. market access for the system.
Amazon’s constellation is categorized with the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) under the name Kuiper Systems. Amazon affirmed its association with Kuiper Systems in an assertion to SpaceNews.
The Effort of Private Companies to make Satellite Constellation Effective
After OneWeb, Starlink, the constellation of the founder of SpaceX Elon Musk, starts its career in orbit while Kuiper, the future constellation of the founder of Amazon and Blue Origin, Jeff Bezos was planned to hit the scene in the mid last year. Five leading investors took an interest in these fundraisers, the most included is Google. These three constellations figured out how to pull in investors notwithstanding doubts about the monetary model.
Altogether, Elon Musk has raised more than two billion American dollars since 2016; this, without considering the last activity in progress, launched in April 2019, for an aggregate of 500,000,000 American dollars. In 2015, Elon Musk clarified that the benefits of Starlink, which he expected thirty billion American dollars of turnover from 2025, would be utilized to fund his future Starship, the completely reusable second stage and spaceship of the SpaceX BFR rocket bound to join the Mars and Moon.
For investors, satellite constellations are known to be a dangerous bet. When the technical issues are solved, how will they bring in cash with clients, though many, however with restricted methods? They are part of the long term and corresponding to the current environment. They bet that the interest in the network will develop to the extent that there will be space for a satellite infrastructure.
Google, for instance, plans to depend on Starlink to launch a real-time streaming game offer. Amazon is relying on Kuiper to “select” new individual and business clients. Amazon has a deal with Lockheed Martin, which will give the ground segment. The satellite information receiving antennas will be near the Amazon server centers that will receive them. The group will have the option to directly offer analysis services and data management to its cloud clients.
Reference:
- https://www.spacelegalissues.com/satellite-constellations-a-race-is-engaged/
- https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Satellite_constellation
- https://www.space.com/spacex-starlink-satellite-megaconstellation-launch-photos.html
- https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/OneWeb_satellite_constellation
- https://www.google.com/amp/s/www.space.com/amp/amazon-plans-3236-satellite-constellation-for-internet.html
- https://www.wired.co.uk/article/spacex-satellite-constellations














